|
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (QMS) – REQUIREMENTS |
|
ARTICLE 1. SCOPE |
While Loran establishes quality management system, its bases on ISO 9001:2018 quality management system requirements, AS9100 Rev.D aviation, space, and defense industry standards and the OEM requirements, definitions, and notes.
|
|
If there is a conflict between the requirements of AS9120 Rev.B Standards and customer or applicable statutory or regulatory requirements, the Customer Requirements and Legal Requirements shall take precedence. This situation may require Configuration Management. |
Loran QMS covers the following topics:
- How all managerial and other processes should be within the scope of Loran management and working environment,
- Keeping the processes and all related stages under record, documenting, and ensuring their traceability,
- Risk - Opportunity management,
- Ensuring personnel participation in the company working discipline,
- Customer relations and satisfaction,
- Supplier relations and management,
- Management decisions and management review meetings,
- Company reports to prevent any fault project management processes,
- Process control, reporting and analysis,
- Delivery and post-delivery relations,
- Analysis of internal and external audit processes and results,
- Analysis of management review decisions and results,
- Establishing corrective action against the problems encountered during the operation of the company and examining the root causes of the problems,
- Human resource management and trainings,
- Customer claims (nonconformity and warranty),
|
ARTICLE 2. NORMATIVE REFERENCES |
The following standards and documents were used as a reference during the preparation of the Quality Management System:
|
Standard and Revision |
Description of the Standard |
|
AS9100 Rev.D |
Quality Management Systems - Requirements for Aviation, Space, and Defense Organizations |
|
AS9120 Rev.B |
Quality Management Systems – Requirements for Aviation, Space, and Defense Distributors |
|
ISO 31000 2018-03 |
Risk Management Guideline |
|
SAE ARP9134 2014 |
Supply Chain Risk Management Guideline |
|
AS9131 Rev.D |
Aerospace Series – Quality Management Systems – NonConformity Data Definition and Documentation |
|
AS13000 2014-5 |
Problem Solving Requirements for Suppliers |
|
SAE ARP9136 2016-11 |
Aerospace Series – Root Cause and Problem Solving (9S Methodology) |
|
AS6832 2020-06 |
Counterfeit Material, Assuring Acquisition of Authentic and Conforming Fasteners |
|
AS6174 Rev.A |
Counterfeit Materiel; Assuring Acquisition of Authentic and Conforming Materiel |
|
AS9163 2022-12 |
Aerospace Series - Certificate of Conformity Requirements |
|
ISO 10002 2018-07 |
Quality management — Customer satisfaction — Guidelines for complaints handling in organizations |
|
ISO 10007 2017 (3RD) |
Quality management — Guidelines for configuration management |
|
ISO-IEC 17025 2017-12 |
General Requirements for the Competence of Testing and Calibration Laboratories |
|
AS9146 2017-04 |
Foreign Object Damage (FOD) Prevention Program - Requirements for Aerospace and Defense Organizations Standard |
|
OTHER PUBLICATIONS |
|
|
Document Reference |
Description of the Document |
|
SAE CMB5 Rev.A 2014 |
Technical Report - Configuration Management Requirements for Subcontractors / Vendors |
|
Lockheed Martin Guidebook Issue 1, Sep. 2022 |
Root Cause Corrective Action Problem Solving Guidebook |
|
SCMH Topic: 7.5 Configuration Management Rev. B 2021 |
7.5.3 Configuration Management Guidelines |
|
ARTICLE 3. TERMS AND DEFINITIONS |
|
Term |
Definition |
|
Article |
Material, part, component, assembly, or appliance which is listed by the design organization as eligible for installation in/on the product or included in the design data approved by the authority. |
|
Authorized Release Certificate |
Document attesting that a product is released for use (e.g., release or return to service) and certifying that the activities performed, and the results achieved, conform to established organization, regulatory, and customer requirements. |
|
Nonconformance |
A condition of any article, material or service in which one or more characteristics do not conform to requirements specified in the contract, drawings, specifications, or other approved product description. Includes failures, discrepancies, defects, anomalies, and malfunctions. Loran Aerospace uses the SAE AS9131 (Rev.D) Aerospace Series - Quality Management Systems - Nonconformity Data Definition and Documentation for Nonconformance processes. |
|
Disposition |
Appropriate action to resolve the nonconformance. |
|
Product Safety |
Maintaining the state of product so that it is able to perform to its designed or intended purpose without causing unacceptable risk of harm to persons or damage to property. |
|
Splitting |
The division of product either physically or by batch quantity, without affecting the product characteristics or conformity. |
|
Test Report |
Documented information that shows objective evidence provided by either the manufacturer or a certified testing facility that the product conforms with specific design requirements, product or performance characteristics. |
|
Unapproved Part |
A part that was not produced or maintained in accordance with approved or acceptable data and applicable statutory, regulatory, and customer requirements. |
|
CAR |
Corrective Action Report |
|
Root Cause |
The fundamental deficiency or failure of a process that when resolved, prevents or significantly reduces the likelihood of recurrence of the problem. |
|
Root Cause Corrective Action |
Root cause corrective action (RCCA) is an effective process for finding the causes of an event and facilitating effective corrective actions to prevent recurrence. |
|
8D Problem Solving |
A problem-solving model establishes a permanent corrective action based on statistical analysis of the problem and focuses on the origin of the problem by determining its root causes. Although it originally comprised eight stages, or disciplines, the eight disciplines system was later augmented by an initial planning stage. The purpose of the 8D methodology is to identify, correct, and eliminate recurring problems, making it useful in product and process improvement. Loran Aerospace uses the SAE AS13000 (2014-05) Problem Solving Requirements for Suppliers Standard for CAR processes. |
|
Failure Event |
The failure event is a description of the problem that Loran team is analyzing. |
|
Supplier |
External provider of goods, processes or services. This may include outsourced services, contract employees, and vendors. The party to the purchase agreement supplying material, parts, assemblies, subassemblies, systems, or services in accordance with the provisions of the purchase order. |
|
Approval Status |
Currently there are three possible approval status designations, i.e., Approved Supplier, Conditionally Approved Supplier, and Cancelled Supplier. |
|
Approved Supplier |
Suppliers whose have a score depending on the on-time delivery and product quality with a minimum of 75 or Maximum 1 product rejection within a year. |
|
Conditionally Approved Supplier |
They are the suppliers classified as supplier can supply the products of Purchase Exceptional or the supplier whose newly starts the work with Loran and will deliver their first products. Their supplier score is between 50-75. |
|
Cancelled Supplier |
Suppliers whose scores are below 50. The cancelled supplier term covers all companies that provide counterfeit products and or forge traceability documents, and or cannot provide adequate technical support and warranty. |
|
Approval Scope |
Approval scope indicates the process(s), product(s), service(s) and/or product/service family(s)for which the supplier is approved. |
|
Purchase Order |
The document that details the entire purchase agreement. These may include, but is not limited to, procurement documents such as contract work orders, purchase agreements and referenced documents such as specifications, trace documentation, maintenance manuals, tear down lists etc. |
|
Supplier Qualification Form |
The main purpose of the supplier qualification form is to help fully understand the risk assessment of the supplier company and the company's capabilities. Every company that wants to do business with Loran must first fill out this form and wait to proceed to the next stage depending on the form evaluation result. Loran supplier qualification form is open to all visitors through Loran's online platforms (https://loranaero.com/supqualification-section1.html). All data is stored and evaluated on the ERP system. |
|
Purchasing Exception |
If the product is not available from another company in the market, or the product is "hard to find", or the customer has a special supplier request for the product, Loran carries out the product order subject to the approval of the Senior Management, except for the supplier being an "approved" supplier. These suppliers are classified as "Conditionally Approved" suppliers for Loran. If traceability is unavailable, or the documentation is suspected of being falsified, Loran discontinues efforts to procure the part. |
|
Traceability |
The traceability term is a capability to track and document the history, location and (if exist) usage of the product or the materials from the manufacturing stage to (if exist) the distributors/suppliers and to the current end-user. |
|
Certificate of Conformity (CoC/CofC) |
It is also known as a Certificate of Compliance or Certificate of Conformance, is a document that verifies that a product or service meets required standards or specifications. The document may include information such as manufacturer, distributor, quantity, lot and/or date code, inspection date, etc., and is signed by a responsible party for the supplier. Loran carries out its policy covering the preparation, preservation and transmission of CoC documents to the customer in accordance with the AS9163 2022-12 Standard. |
|
Certificate of Origin (CoO) |
It is an origin country declaration for supplied product. |
|
Materiel |
In our QMS, refers to material, parts, assemblies, and other procured items (except for electronic and chemical parts). |
|
Manufacturer |
In our QMS, refers to the point of origin of any materiel covered by the standard, including factories, mills, foundries, mines, chemical plants, laboratories, etc. |
|
|
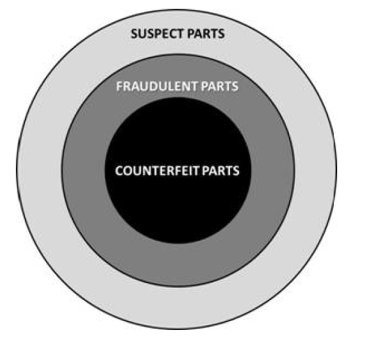
Suspect Materiel: Materiel, items, or products in which there is an indication by visual inspection, testing, or other information that it may meet the definition of fraudulent materiel or counterfeit materiel provided below. |
|
Fraudulent Materiel: Suspect materiel misrepresented to the customer as meeting the customer’s requirements. |
|
|
Counterfeit Materiel: Fraudulent materiel that has been confirmed to be a copy, imitation or substitute that has been represented, identified, or marked as genuine, and/or altered by a source without legal right with intent to mislead, deceive or defraud. |
|
|
Identity |
Information such as the current design authority, original manufacturer, trademark or other intellectual property, performance, unique item identifier, part number, date code, lot number, testing methods and results, inspection, documentation, warranty, origin, ownership history, packaging, storage, handling, physical condition, previous use, etc. |
|
Authentic |
Produced with legal right or authority granted by the legally authorized source. |
|
Aftermarket Manufacturer |
A manufacturer that meets one or both of the following criteria:
|
|
Approved Supplier |
Suppliers that are formally assessed by the current design activity or the original manufacturer, determined to be a trusted source that will reliably provide authentic and conforming materiel, and entered on a register of approved suppliers. |
|
Authorized Reseller |
An entity who has a legally binding relationship with the legally authorized source but does not provide direct product support to the customer. |
|
Authorized Supplier |
Aftermarket manufacturers as defined above, and suppliers authorized by the current design activity or the original manufacturer to produce and/or sell materiel. |
|
Certificate of Authenticity |
A statement to the effect that all materiel items listed above furnished on this contract are genuine, new and unused unless otherwise specified in writing herein; are suitable for the intended purpose; are not defective, suspect, or counterfeit; have not been provided under false pretenses; and have not been materially altered, damaged, deteriorated, or degraded. |
|
Disposition |
Decisions made by authorized representatives within an organization concerning future treatment of nonconforming material. Examples of dispositions are to scrap, mutilation, use-as-is (normally accompanied by an approved variance/waiver), retest, rework, repair, or return-to-supplier. |
|
Original Manufacturer |
An organization that designs and/or engineers and produces material and is pursuing or has obtained the intellectual property rights to that material. Notes:
|
|
Supply Chain Traceability |
Documented evidence of materiel’s supply chain history. This refers to documentation of all supply chain intermediaries and significant handling transactions, such as from original manufacturer to distributor, or from excess inventory to broker to distributor. |
|
Heat Number |
The heat number is used to trace the material's origin to ensure metal quality. It's similar to a batch number as it relates to quality control in manufacturing facilities. This number should match the number that is printed or stamped on the surface of the material. |
|
Uncertainty |
Lack of understanding of an event or its knowledge, outcome or probability. It should not be confused with measurement uncertainty. |
|
Risk |
Negative impact of uncertainty |
|
Opportunity |
The positive effect of uncertainty |
|
Controlled Document |
All documents reviewed and approved before they are published for use or reference. |
|
UN-Controlled Document: |
All documents or forms which are need to approval before the use. |
|
Interested Party |
The companies who buy the products from Loran, or the companies who supply the products to Loran, or any parties which have in a relationship with Loran Aerospace. |
|
Foreign Object Damage (FOD) |
All kinds of non-process tools, consumables, equipment, product protective devices, personal items, product process wastes, operational wastes, environmental residues are considered as foreign objects as Damage Objects. |
|
Configuration |
It is a documented information covers the technical and physical specifications of the product. This documented specs are open for the distributors and customers, to avoid any fault or mis-ordering process. |
|
Configuration Management |
It is a discipline to keep, manage and reports the records, technical and physical revisions for a product in its lifecycle. |
|
Calibration |
Calibration is the process of configuring an instrument to provide a result for a sample within an acceptable range. |